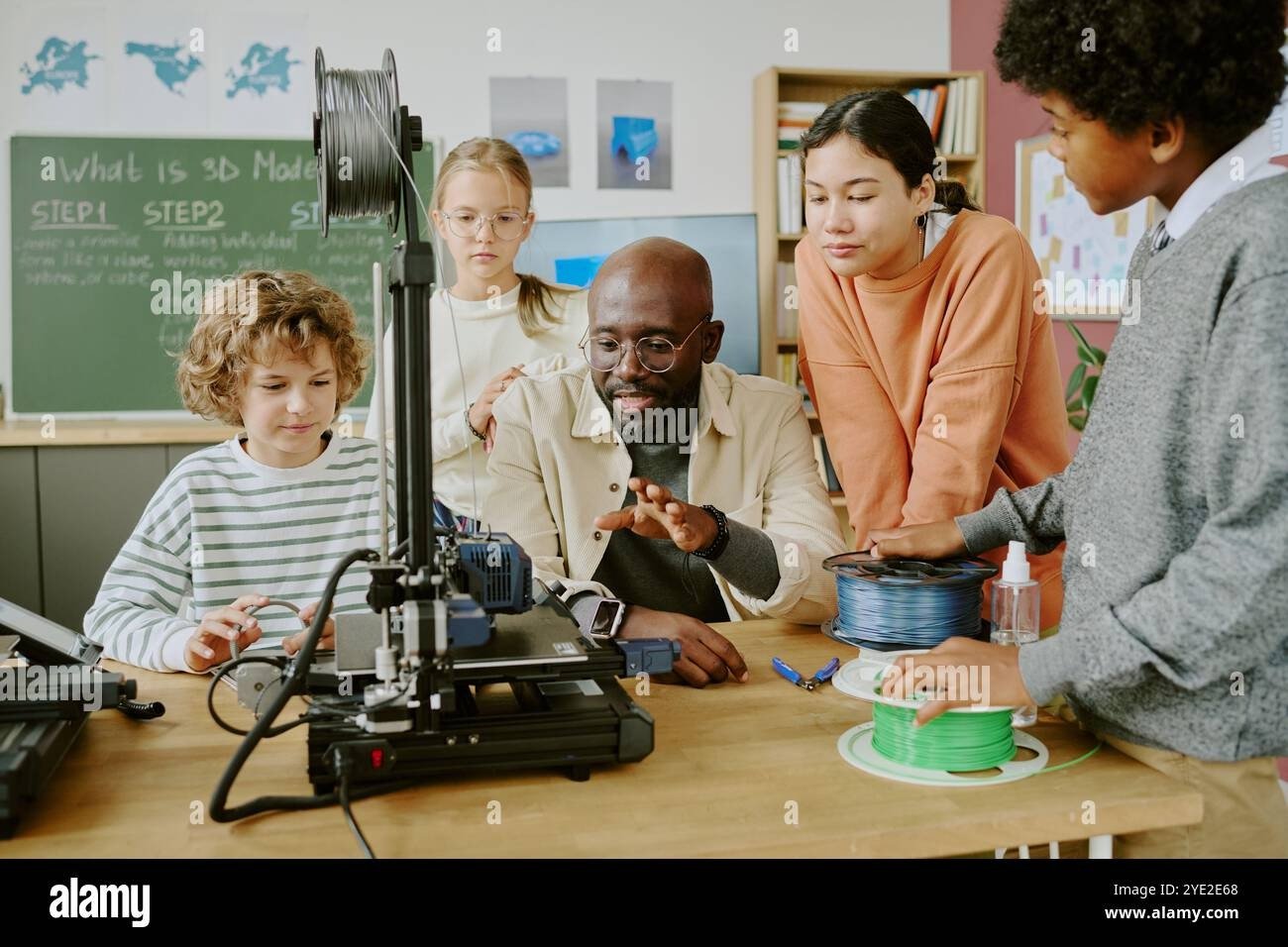
Manufacturing Across Grades K-5: From Makers to Innovators
Overall Learning Progression
Students move from understanding how machines work for us, to designing and producing purposeful, functional products using manufacturing tools.
—
Grade – Machines & Our Ideas
Core Concepts and Learning Progression
In K-1st Grade, students begin by understanding that machines are tools that assist us in creating things, extending human abilities. This progresses to students learning how to give instructions to machines to produce specific items from their own designs. The focus is on appreciating the design process and recognizing the direct link between their ideas and physical outcomes. By the end of this stage, students can explain how machines help make things and can design simple items.
I Can: I can explain that machines can help people make and create things.
I Can: design something that a machine can make.
Example Units and Lessons
Draw Game Pieces and 3D Animals
Use simple draw tools on tablets or Chromebooks to design shapes, pictures, animals, or logos.
Watch as the teacher uses a 3D printer, laser engraver, or Cricut to turn their digital designs into stickers, animal cutouts, or name tags.
Introduce the concept of "input → output": our ideas go into the machine, and products come out.
Standards Integration
NGSS Connection: K-2-ETS1-1 — Ask questions and make observations to define a problem.
NGSS Connection: K-2-ETS1-2 — Develop sketches or models to show how to solve a problem.
Core Concepts and Learning Progression
In 2nd and 3rd grade, students transition from observing machines to actively creating using digital design tools. They learn to design products with the intent for machine production, focusing on understanding concepts like scale, size, and structure. By this stage, students are able to use digital tools to design and produce their own products.
Example Units and Lessons
Introduction to CAD Tutorials
Learn about scaling, measurements, and proportions so items print or cut correctly. Understand basic 3D printing design rules — no floating parts or overhangs. Introduce testing and refinement: redesign if something doesn't print or fit correctly.
Creating 3D Key Chains
Students use Tinkercad, Cricut Design Space, or similar software to create their own projects, such as custom keychains, classroom nameplates, or small figurines.
Standards Integration
NGSS Connections:
2nd: K-2-ETS1-3 — Analyze data from tests to improve a design.
3rd: 3-5-ETS1-1 — Define a problem with specific criteria and constraints.
—
I Can: I can use digital tools to design and make my own product.
Grade – Becoming Digital Makers
Grade – Designing for a Purpose
Core Concepts and Learning Progression
Students move from basic creation to designing with a specific purpose. They learn to create meaningful and functional items that solve problems or fulfill needs. This involves understanding design thinking in digital manufacturing, where technology is used purposefully to bring ideas to life, emphasizing the creation of detailed digital blueprints and models before physical manufacturing.
I Can: I can design and make something that is both useful and meaningful.
Example Units and Lessons
Create 3D printed functional item
Students create items with specific functions or personal meaning, exploring the idea of form and function – how a design should not only look good but also work well.
CAD Modeling and Blueprints: Students learn to use CAD software to create precise digital models and blueprints, understanding how these digital designs translate into physical objects through manufacturing processes.
Examples: jewelry holders, phone stands, or organizers for pencils and markers.
Personal Crests or Minecraft characters
Students design laser engraved personal crests or keychains, connecting their identity to their designs.
Standards Integration
NGSS Connection: 3-5-ETS1-2 — Generate and compare multiple possible solutions based on criteria and constraints.
Reflection: How does your design help someone or solve a problem?
Example Units and Lessons
Grade – Innovating with Movement and Function
Core Concepts and Learning Progression
At this level, students integrate creativity, electronics, and functionality, viewing manufacturing as innovation. They develop empathy-driven engineering skills, focusing on how their creations can make a meaningful impact in the world by solving real problems. This involves advanced making, combining mechanical and electronic elements to engineer solutions that make a tangible difference. This also includes advanced CAD designing, where students create digital models and detailed technical drawings before manufacturing complex projects. They begin to understand that engineering and manufacturing can be viable career paths, offering opportunities to earn a living while solving real-world problems and creating positive change.
Interactive 3D Print
A desk light or toy with LEDs and a button.
Laser-Cut + Cricut Combo Project
Engraved kindness coins with details.
I Can: I can design and make a product that includes moving or interactive parts.
Standards Integration
NGSS Connection: 3-5-ETS1-3 — Plan and carry out fair tests to refine a design.
Reflection: How can I integrate moving or interactive elements into my design?
Mechanical Model
Students use advanced CAD software to design two-part hinge systems or moving gear assemblies, creating detailed digital models and technical drawings before physical manufacturing.
Assistive Device Challenge
Design something that makes a daily task easier.